You're on:
Home Blog The Connection Between Knee Pain and Posture: What You Need to Know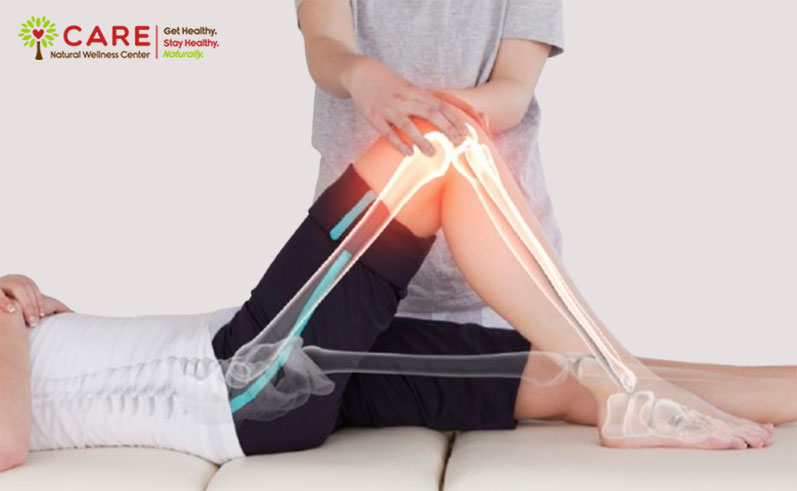
The Connection Between Knee Pain and Posture: What You Need to Know
Overview:
Knee pain is a common ailment that affects people of all ages, and while injuries and overuse are well-known culprits, poor posture is often an overlooked factor. The way we stand, sit, and move can have a profound impact on knee health, as posture influences the alignment and mechanics of the entire musculoskeletal system. Understanding this connection is essential for prevention and effective management of knee pain.
How Posture Impacts Knee Health
The knees serve as a vital link in the kinetic chain of the body, connecting the hips and ankles. When posture is misaligned, it creates uneven distribution of forces across the knee joint. This can lead to excessive stress on certain structures, such as the ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Over time, this imbalance may contribute to conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome, osteoarthritis, or chronic inflammation.
For instance, poor posture such as slouching or forward head tilt can shift the body’s center of gravity, placing extra strain on the knees. Similarly, flat feet or inward knee alignment (valgus posture) can increase the risk of joint damage due to improper load distribution.
Common Postural Issues Linked to Knee Pain
1. Pelvic Tilt: An anterior or posterior pelvic tilt can alter the angle of the femur and tibia, leading to inefficient knee mechanics.
2. Knock-Knees (Genu Valgum): Inward knee alignment stresses the medial ligaments and cartilage.
3. Bowlegs (Genu Varum): Outward knee alignment can overload the lateral structures of the knee.
4. Flat Feet (Overpronation): This can cause the knees to collapse inward, disrupting the natural alignment of the legs.
Symptoms of Posture-Related Knee Pain
· Persistent aching or sharp pain around the knee.
· Swelling or stiffness, especially after prolonged standing or walking.
· Difficulty in straightening or bending the knee fully.
· Discomfort that improves with adjustments in posture or footwear.
Preventing and Managing Knee Pain Through Postural Corrections
1. Ergonomic Adjustments: Use supportive seating and maintain proper desk height to encourage upright posture during work.
2. Strengthening and Stretching: Engage in exercises targeting the core, glutes, and leg muscles to support joint stability and alignment.
3. Footwear: Opt for shoes with adequate arch support to prevent overpronation and improve gait mechanics.
4. Professional Assessment: Seek guidance from a physical therapist or chiropractor to identify and correct specific postural deviations.
5. Mindfulness: Incorporate habits like standing tall, aligning the head over the shoulders, and keeping the knees slightly bent rather than locked during prolonged standing.
Conclusion
Good posture plays a crucial role in maintaining knee health by ensuring proper alignment and load distribution. Poor posture can silently contribute to knee pain, but with awareness and targeted interventions, it is possible to prevent or alleviate discomfort. Prioritizing postural health is not only beneficial for your knees but for the entire body, paving the way for improved mobility and quality of life.
More Posts
